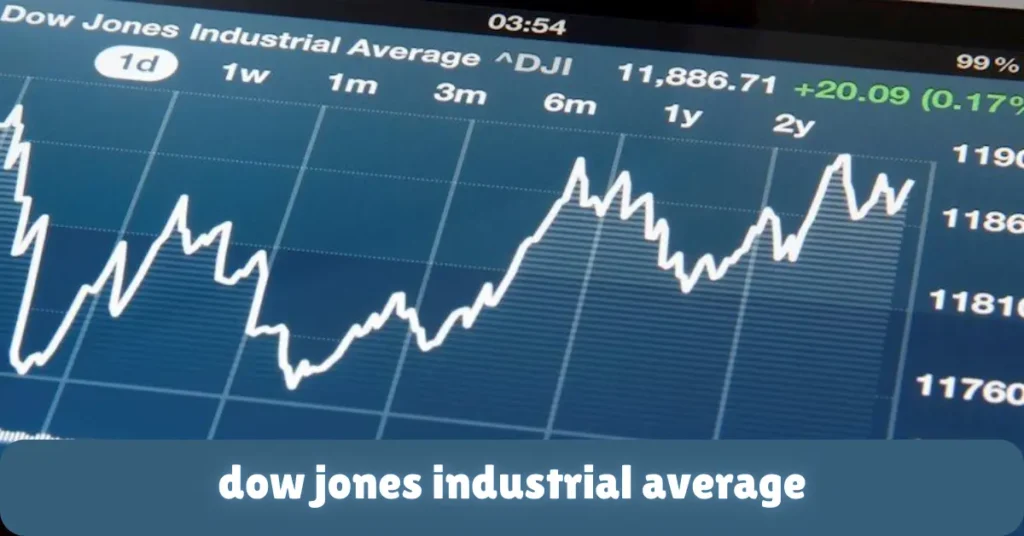
Introduction
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is one of the most well-known stock market indices in the world. But what exactly does it represent? Simply put, the Dow tracks the stock prices of 30 major companies in the United States, helping us understand how the overall stock market is performing. When people talk about the “stock market going up or down,” they are often referring to the movement of the Dow.
Created in 1896 by Charles Dow, the DJIA has become a key indicator of the health of the U.S. economy. It’s widely used by investors, financial experts, and even the media to gauge how things are going in the stock market. In this article, we’ll break down what the Dow is, how it works, and why it matters to both investors and the general public.
What is the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 30 major publicly traded companies in the United States. These companies are leaders in their industries and represent a broad range of sectors, such as technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer goods.
The Dow was created by Charles Dow in 1896 to give people a snapshot of how the stock market was performing. It is often used as a benchmark to gauge the overall health of the U.S. stock market and economy. While the Dow only includes 30 companies, it is one of the most widely followed indices globally and often quoted in the news.
Unlike other indices that are weighted by market value, the Dow is a price-weighted index, meaning the companies with the highest stock prices have the most influence on the index’s movement. This makes it unique compared to other indices like the S&P 500, which is weighted by market capitalization.
You May Also Like It
Trendzguruji.me – Computer, Cyber, Awareness, SEO, Health & Beauty Guide
TrendzGuruji.me Cyber Insights Hub
“What’s Up with Emerald Gems? Let’s Talk
Why is the Dow Jones Industrial Average Important?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) plays a significant role in the financial world. Here’s why it’s so important:
Snapshot of Market Health
- The DJIA serves as a quick and reliable indicator of the overall performance of the U.S. stock market.
- When the Dow rises or falls, it often reflects how the broader economy is doing, as it tracks major companies in various industries.
Investor Sentiment
- The Dow is a barometer of investor confidence.
- If the Dow is rising, it typically means that investors are optimistic about the economy and corporate profits.
- A falling Dow may indicate uncertainty or negative outlooks from investors.
Reflects Major U.S. Industries
- The 30 companies in the Dow are leaders in their industries, including sectors like technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer goods.
- These industries make up a significant portion of the U.S. economy, so the Dow gives a broad view of its performance.
Easy to Track
- The Dow is simple to understand and widely quoted in the media.
- It’s an accessible measure of stock market trends for the general public, even for those with limited knowledge of investing.
Used as a Benchmark
- The DJIA is often used by investors and financial analysts as a benchmark to compare the performance of their own investments or portfolios.
- It provides a standard to measure how well the stock market is doing compared to other individual stocks or funds.
Influences Media and Public Perception
- News outlets and financial experts frequently refer to the Dow when discussing market movements.
- Because of its high visibility, the DJIA can influence public perception of the economy, even though it only represents 30 companies.
Economic Indicator for Policymakers
- The movement of the Dow is closely monitored by policymakers, such as the Federal Reserve, to help assess the health of the economy.
- A significant drop in the Dow may lead to actions like lowering interest rates or other measures to stimulate economic growth.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)

Here’s a simple, step-by-step guide to help you understand the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), how it works, and why it matters.
Step 1: Understand What the Dow Is
- Definition: The Dow Jones Industrial Average is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 30 large, publicly traded companies in the United States.
- Purpose: It serves as a snapshot of the U.S. stock market and is often used as an indicator of how the economy is doing.
Step 2: Learn How the Dow is Calculated
The Dow is a price-weighted index, which means the stock price of each company in the index directly impacts its value.
- Price-Weighted: The higher the stock price of a company, the greater its impact on the Dow’s overall movement. This is different from other indices, like the S&P 500, which are weighted by market capitalization.
The formula is:
DJIA
- Sum of stock prices of 30 companies
- Dow Divisor
- DJIA=
- Dow Divisor
- Sum of stock prices of 30 companies
The Dow Divisor adjusts the index to account for stock splits, dividends, and other factors.
Step 3: Know the Companies in the Dow
The Dow includes 30 major companies from various sectors like technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods.
These companies are considered leaders in their industries and have a significant impact on the U.S. economy. Some examples of companies in the Dow include:
- Apple
- Microsoft
- Coca-Cola
- Johnson & Johnson
- Boeing
Step 4: Understand Why the Dow is Important
- Market Indicator: The Dow provides a quick and accessible measure of how the overall stock market is performing.
- Investor Sentiment: A rising Dow typically indicates optimism among investors, while a falling Dow can signal concerns about the economy.
- Benchmark for Investors: Investors use the Dow as a reference to compare the performance of their portfolios or individual investments.
Step 5: Know How the Dow Affects the Economy
- Economic Snapshot: The Dow is often used by policymakers to understand the overall health of the economy.
- Market Trends: A significant drop in the Dow can signal economic trouble, prompting government action, such as lowering interest rates.
- Public Perception: The Dow is widely covered by the media and influences public perception of the U.S. economy.
Step 6: Watch the Dow’s Performance
- The Dow’s performance is reported daily, showing whether it has gone up or down.
- You can track the Dow’s performance on financial news websites, apps, or by checking reports in the media.
- Keep in mind, that while the Dow is important, it only represents 30 companies, so it may not always reflect the performance of the entire stock market.
Step 7: Recognize the Limitations of the Dow
- The Dow only includes 30 companies, so it doesn’t provide a complete picture of the entire stock market.
- It’s also price-weighted, which means that a company with a high stock price (even if it’s not the largest by market value) can have a larger impact on the Dow’s movement than a smaller company with a lower stock price.
Step 8: Compare the Dow with Other Indices
- S&P 500: Includes 500 large companies and is market-cap-weighted, meaning larger companies have more influence on the index.
- Nasdaq Composite: Heavily weighted toward tech companies and also includes thousands of companies, offering a broader view of the tech sector.
Step 9: Understand Dow Updates
- Companies may be added to or removed from the Dow, based on their performance or changes in the economy.
- The changes are made by a committee of editors at The Wall Street Journal and are based on factors like the company’s size, reputation, and economic impact.
Step 10: Track the Dow’s Impact on Your Investments
- Even if you don’t invest directly in the Dow, watching its movements can help you make informed decisions about your investments.
- The Dow is a good starting point for understanding broader market trends, but it should not be the only index you follow.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a widely followed stock market index, but like any financial tool, it has both advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a breakdown:
Advantages
| Simple and Easy to Understand The Dow is a price-weighted index, making it easier to track and understand for people who are new to investing or don’t have in-depth knowledge of the stock market. It’s often used in the media and provides a quick snapshot of the overall market’s performance. |
| Represents Major U.S. Companies The Dow tracks 30 large, influential companies that span various sectors, such as technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods. This gives investors a broad view of key industries in the U.S. economy. |
| Widely Recognized and Followed It is one of the most widely followed stock market indices, making it an important benchmark for investors, policymakers, and financial experts. The performance of the Dow is often reported in the news, making it easy for anyone to follow the state of the stock market. |
| Historic and Reliable Indicator The Dow has been around for over 100 years, providing a long track record of how the U.S. economy has evolved over time. This historical perspective can be valuable for understanding broader market trends and making long-term investment decisions. |
| Benchmark for Portfolio Performance Many investors use the Dow as a benchmark to compare the performance of their own portfolios or individual investments. It allows them to see if their investments are performing better or worse than the market as a whole. |
Disadvantages
| Limited Representation The Dow only tracks 30 companies, which is a very small number compared to broader indices like the S&P 500 (which tracks 500 companies). As a result, it doesn’t reflect the full spectrum of the stock market, especially when it comes to emerging industries or smaller companies. |
| Price-Weighted Structure The Dow is a price-weighted index, meaning that companies with higher stock prices have a greater influence on the index, regardless of their actual size or market value. This can lead to an unbalanced representation of the market. For example, a small company with a high stock price could affect the Dow more than a much larger company with a lower stock price. |
| Lack of Diversity in Sectors While the Dow represents a variety of sectors, it is still heavily weighted toward certain industries like technology, finance, and consumer goods. It may not accurately represent sectors that are underrepresented, such as small-cap stocks or emerging industries like clean energy. |
| Not Reflective of the Entire U.S. Economy While the Dow gives a good sense of how large, established companies are performing, it doesn’t give a full picture of the entire U.S. economy. For example, it doesn’t include small businesses, which make up a large portion of the economy, nor does it account for international market influences on U.S. companies. |
| Subject to Changes The companies included in the Dow can be updated or changed over time, which means that its composition can shift depending on the performance and economic relevance of the companies. This can sometimes lead to sudden changes in the index that may not necessarily reflect the broader market’s health. |
You May Also Like It!
Margie Washichek – A Comprehancive Guide – Veganov Trichy
Seargeoh Stallone – Complete Guide – Veganov Trichy
I Fear No One, But Respect Everyone. – Tymoff – Complete Guide – Veganov Trich”
Common FAQs About the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), answered in simple and easy-to-understand language.
What is the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
Why is the Dow important?
How is the Dow calculated?
What does it mean when the Dow goes up or down?
How often is the Dow updated?
How do companies get added to or removed from the Dow?
What types of companies are in the Dow?
Technology (e.g., Apple, Microsoft)
Healthcare (e.g., Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer)
Finance (e.g., JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs)
Consumer Goods (e.g., Coca-Cola, McDonald’s)
These companies are leaders in their industries and reflect the broader U.S. economy.
How does the Dow differ from other stock market indices?
Can I invest in the Dow Jones Industrial Average directly?
Is the Dow a good indicator of the stock market?
Conclusion
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a key indicator of the U.S. stock market, tracking the performance of 30 major companies. It helps investors and the public understand how the economy is doing by reflecting the trends in large, influential industries. While it’s an important tool, the Dow only represents a small portion of the market, so it’s best used alongside other indices for a fuller picture. By keeping an eye on the Dow, you can get a sense of market health and investor sentiment.
Bonus Points About the Dow Jones Industrial Average
Here are some extra interesting facts and insights about the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) that you might find useful:
Oldest Stock Market Index
- The Dow is the oldest major stock market index, created in 1896 by Charles Dow, the co-founder of The Wall Street Journal.
Regularly Adjusted for Stock Splits
- The Dow Divisor, which is used in the calculation of the index, is adjusted whenever stock splits or other major events occur. This ensures the index remains accurate and consistent over time.
Represents a Cross-Section of the Economy
- The 30 companies in the Dow span a wide range of industries, making it a useful indicator of the broader U.S. economy. However, it does not include every sector, such as real estate or utilities, which means it doesn’t give a full picture of all sectors.
Has Seen Some Iconic Moments
- Over its long history, the Dow has experienced major milestones, like breaking the 1,000-point barrier in 1972, surpassing 10,000 points in 1999, and reaching 30,000 points in 2020.
Not Always Perfect for Predicting Trends
- Because the Dow only tracks 30 companies, it can sometimes be skewed by the performance of one or two companies with higher stock prices. This makes it less reflective of the broader market compared to other indices like the S&P 500.
Known for “Dow 30”
- The Dow is often referred to as “Dow 30” because it includes exactly 30 companies. These companies are meant to represent the economic backbone of the country, although they can change over time based on market conditions.
You May Also Like It!
Bestadvise4u.com News – Complete Guide – veganov Trichy
Tex9.net – Depth – Guide – Veganov Trichy
ICC 22 Jul 2022 West Indies Vs India Viewing Option – Veganov Trichy
Trendzguruji.me – Computer, Cyber, Awareness, SEO, Health & Beauty Guide